Very Summarized Notes on Fluid Statics
Pressure in Static Fluids
A fluid is a collection of matter that is not a solid. That is, the
particles that comprise the matter are not strongly bound to each other
in a fixed lattice. This includes the liquid, gaseous, and even plasma
states of matter. We will actually need to restrict the properties of
the fluids we examine to some extent, so that we can get some
approximate results, but the usefulness of the applications of these
models cannot be overstated.
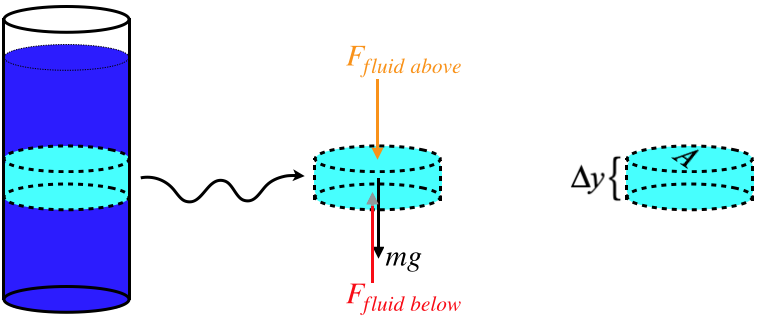
A key property in all fluids is pressure. Consider a container of fluid
in a gravitational field. If we draw a free-body diagram for a small
section of that fluid (and exclude the horizontal forces), then three
forces come to mind: The force of gravity on that section, the amount
that the fluid above that section pushes down on it, and the amount that
the fluid below that section pushes up on it. This diagram is really no
different from one we would draw for a book in the middle of a stack of
books.
The forces from the fluid above and below is therefore equal to the pressures of the fluid above and below multiplied by the cross-sectional areas, and the zero net force from the FBD gives: \(\left. \begin{array}{l} F_{fluid\;above}=P_{above} A \\ F_{fluid\;below}=P_{below} A \end{array} \right\} \;\;\; \Rightarrow \;\;\; P_{below}A=P_{above}A+mg\) As we can readily see, the pressure varies with position in a fluid (namely, at differing heights) in the presence of gravity, even though the fluid is in equilibrium.
Pascal’s Principle
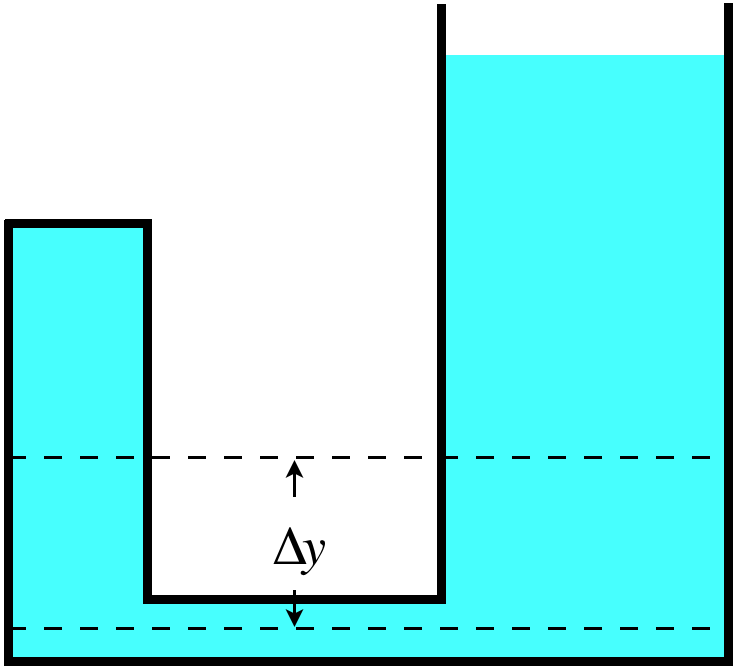
We can rearrange things in the equation above so that the pressure difference between two heights in the fluid are related to the density of the fluid. \(P_{below}=P_{above} + \dfrac{mg\Delta y}{A\Delta y} =P_{above} + \dfrac{mg\Delta y}{V} = P_{above} + \rho g\Delta y\) The nice thing about this result is that it directly compares two pressures, and doesn’t rely upon a choice of a particular disk of fluid for our free-body diagram. This means that if we choose a disk that has less cross-sectional area (but with the same thickness), we find the same difference in pressure. In other words, it turns out that the pressure difference at two depths only depends upon the density of the fluid and the difference in height between the two depths.
For example, suppose we have a fluid confined to a container like the one shown in the figure above. Well, naturally the same analysis applies to both sides of this container, so the pressure difference is the same on both sides. Here we need to invoke the principle that pressure does not have a direction. That is, whatever the pressure is at the bottom of $\Delta y$, that results in a force pushing up on the section of fluid, it also results in a force pushing on a segment of fluid to the side of the position in question. That lateral segment is static just like the remainder of the fluid, so the pressure on both sides must be equal, which means that the pressure is the same everywhere along the lower dashed line.
The Hydraulic Lift
Due to the reasons stated above, when a force is applied to a contained,
incompressible fluid, the pressure increases equally in all directions
throughout the fluid. This fundamental characteristic of fluids provides
the foundation for hydraulic systems found in barbershop chairs,
construction equipment, and the brakes in your car.
The result we obtained above compares the pressure at any two points in
the fluid, but by far the most common comparison is between the pressure
at the top surface of the fluid and the pressure at some depth below
that surface. Calling the pressure at the surface $P_o$ and the depth
below that surface $d$, our equation can be modified to become
\(P\left(d\right)=P_o+\rho g d\) The top surface of the fluid may just
be exposed to the atmosphere, in which case $P_o$ is simply atmospheric
pressure. But the fluid could also be confined by a piston, which leads
to an interesting application called a hydraulic lift. The idea is to
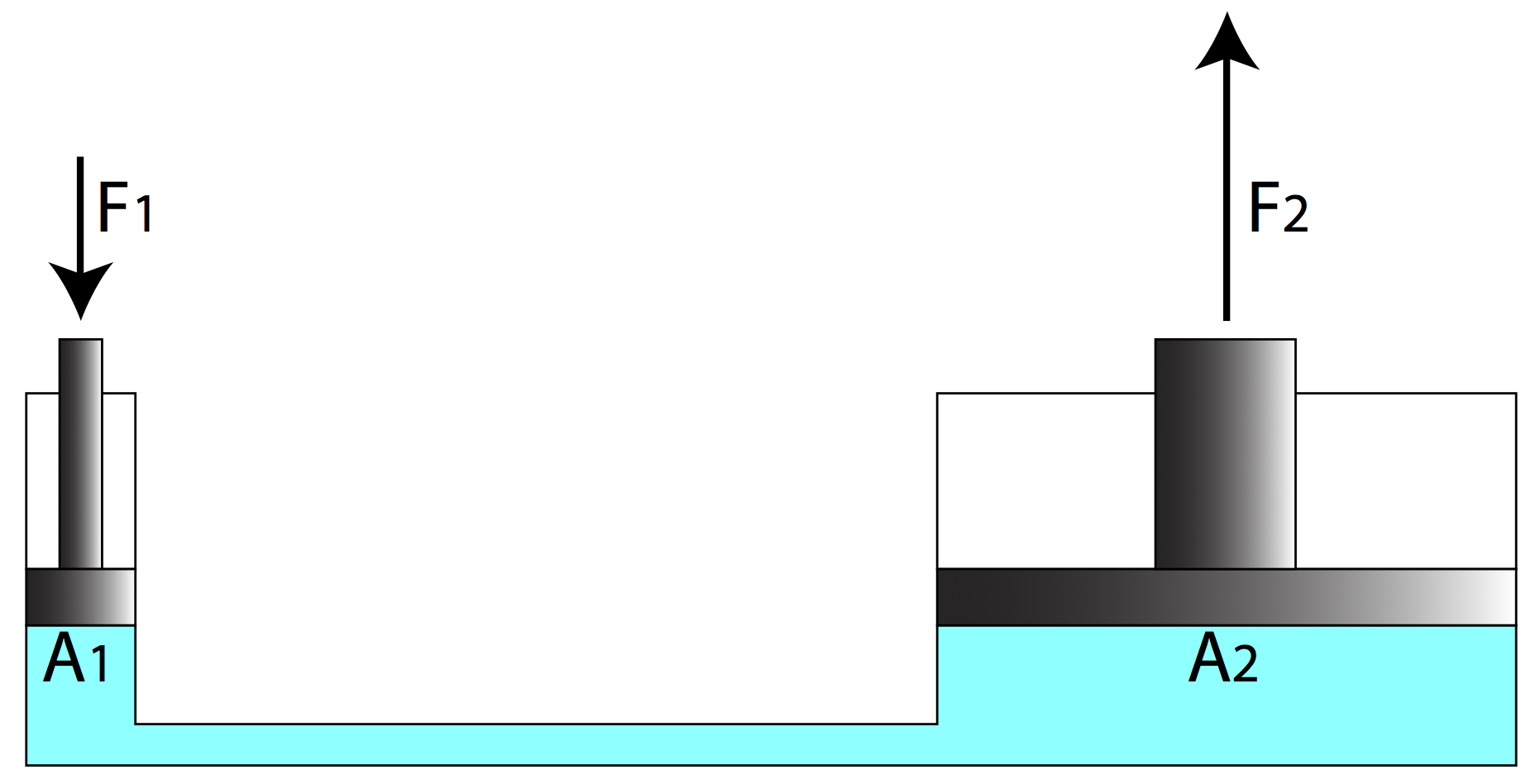
confine the liquid with pistons of different areas on opposite ends of a
continuous fluid, as shown in the following figure.
With the bottom surfaces of the two pistons in contact with the same continuous fluid at the same height, the pressure of the fluid is the same at both surfaces. The forces exerted by the fluid on the two pistons are not the same, however, because the areas are not equal. With pressures equal at both ends, the fluid exerts more force on the piston with a larger area, which means a heavier weight on the larger piston is balanced by a lighter weight on the other piston. This allows for a mechanical advantage in lifting a heavy weight with far less force than the weight, determined by the ratio of the piston areas: \(P_1 = P_2 \implies \dfrac{F_1}{A_1}=\dfrac{F_2}{A_2}\)
Manometers & Barometers
Pascal’s law also gives us a way to measure unknown pressures by
comparing them to known values. A generic device of this kind is called
a manometer. There are many specialized devices designed to measure
specific pressures, such as a barometer (which measures the pressure of
the atmosphere), and a sphygmomanometer (which measures blood
pressure).
The simplest designs for manometers involve exposing one end of a
continuous confined liquid to the region for which the pressure is to be
measured, and the other end to a vacuum (i.e. a region where the
pressure is effectively zero), then measure the difference in height of
the two columns of the liquid and use the liquid’s known density to
compute the pressure difference. For example, here is a simple
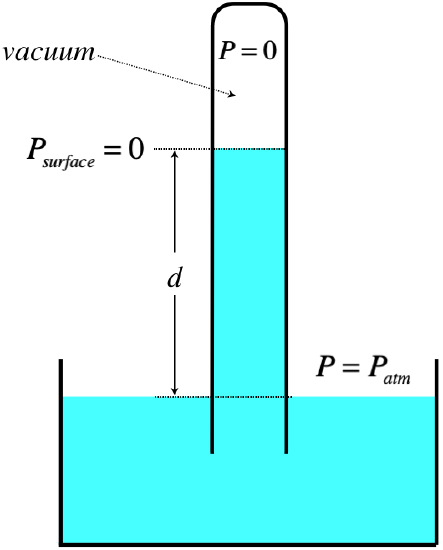
barometer:
In the figure above, the fluid is exposed to the atmosphere in the large
tub, and the top of the vertical tube is evacuated. This is most easily
achieved by filling the tube with the fluid, covering the open end,
inverting it in the tube, then uncovering the open end so that the fluid
runs out until equilibrium is reached. Applying Pascal’s law, the
pressure of the atmosphere at the exposed surface is the same as within
the column at the same height, and applying our equation for pressure at
depth, we have: \(P_{atm}=P_o+\rho g d = \rho g d\) Thus, we can measure
the pressure of the atmosphere by measuring the height of the column of
fluid and knowing its density. Note that this means that there is a
maximum height to which we can raise this column by evacuating the space
above it.
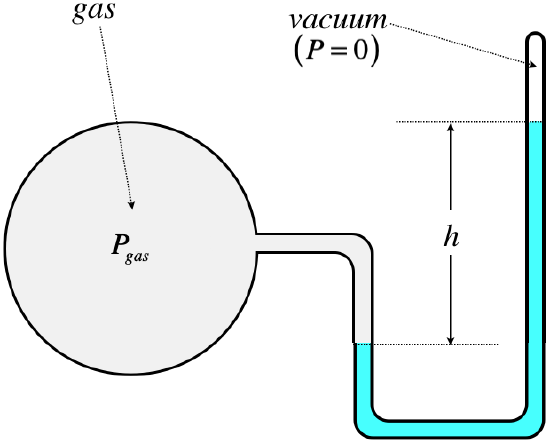
Here is a simple design for a simple gas pressure manometer (i.e. for
enclosed gases of any variety, not just the atmosphere):
When the pressure is measured in this manner, we say that it is the absolute pressure that is measured. It seems silly to add the unnecessary extra word "absolute," but there is a practical reason for this. When it comes to gauges that measure pressure of gases in industrial applications, what the operator of a machine wants to know is if the pressure is close to exceeding the capacity of the device confining the gas. Well, any pressure acting from outside the device is helping to keep it from exploding, so what is needed is the pressure difference between the trapped gas and what is outside. We can measure this directly using the device above by opening the top of the tube so that there is no longer a vacuum there. Then the column height measures the difference between the trapped gas and the ambient pressure. This measurement of pressure is called gauge pressure. There is an analogy here with temperature – absolute temperature is measured on the kelvin scale, and zero is as low as it can go. The celsius scale has the same grading as kelvins, but puts the zero point at the freezing point of water, thus allowing for negative values. Similarly, gauge pressure places the zero point at the ambient (typically atmospheric) pressure, also allowing for a negative value of the pressure measurement.
Archimedes’ Principle
We concluded in the previous section that the pressures on top and bottom differed just enough to balance the weight of the section of fluid, so we know precisely what the resulting force of this unbalanced pressure is – it is the weight of the fluid that would be in that section if the solid object was not there. Put concisely, we have
::: {.epigraph} The buoyant force on an object in a fluid equals the weight of the fluid displaced by that object.
Archimedes’ Principle :::
As simple as this seems, it is very easy to get confused about this force. The main source of confusion tends to be distinguishing the buoyancy force from the net force on the object (which also experiences gravity). Here are some secrets to winding one’s way through the daunting mazes commonly encountered regarding buoyancy:
-
Keep in mind that buoyancy is just the force from the fluid on the object – it is completely independent from the gravity force on the object, and it is not the net force. Draw force diagrams whenever possible, with separate force vectors for gravity and buoyancy, and apply Archimedes’s principle only to the buoyancy force vector.
-
Apply Archimedes’s principle very strictly – the volume of fluid displaced does not always equal the volume of the object (it has to be completely submerged for that).
-
Be careful about drawing conclusions based on the density of the object only – whether an object sinks or floats, it experiences the buoyancy force described by Archimedes’s principle.
Assuming the object in the fluid is completely submerged, then its full volume displaces fluid. This means it feels a buoyancy force equal to the weight of fluid that occupies that same volume. The net force on such an object is the buoyancy force up minus the gravity force down, so if the object weighs more than the displaced fluid, it sinks. Given that the object and the displaced fluid have equal volumes, we can just as easily compare their mass-to-volume ratios to determine which is heavier. This ratio for the fluid is simply its uniform density. For the object, it is its average density. The distinction is that the object may, for example, be hollow. This explains how an aircraft carrier, made of materials significantly denser than water, can float – the hollow parts of the vessel that contain only air reduce its average density greatly.
This is shared under a CC BY-SA 4.0. Slightly modified from UCSD 9B for Seniors at St. John Baptist De La Salle Catholic School, Addis Ababa.
Download the notes as a PDF
To download and read a PDF version of the notes as a PDF, visit the link below